Page 32 - Mirjam-Theelen-Degradation-of-CIGS-solar-cells
P. 32
Chapter 2
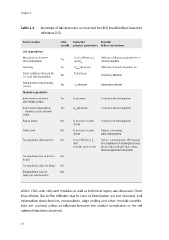
Table 2.2: Summary of failure modes as observed for CIGS (modified but based on
reference [15]).
Failure modes CIGS Impacted Possible
specific physical parameters failure mechanisms
Cell degradation
Main junction: increase Yes Loss in fill factor, J sc Diffusion of dopant, impurities etc +
of recombination and V oc electromigration
Shunting Yes R shunt decreases Diffusion of metals, impurities etc.
Series resistance increase by Yes R s increases Corrosion, diffusion
TCO and Mo degradation
Delamination of back metal Yes J sc decrease Lamination stresses
contact
Module degradation
Interconnect resistance Yes R s increases Corrosion, electromigration
(ZnO:Al/Mo or Mo)
Interconnect degradation Yes R sh decreases Corrosion, electromigration
– shunting: across isolation
scribe
Busbar failure No R s increase or open Corrosion, electromigration
circuit
Solder joint No R s increase or open Fatigue, coarsening
circuit (alloy segregation)
Encapsulation delamination No Loss in fill factor, J sc Surface contamination, UV degrada -
and tion, hydrolysis of silane/glass bond,
possible open circuit warped glass, ‘dinged’ glass edges,
thermal expansion mismatch
Encapsulation: loss or hermet - No
ic seal
Encapsulation: glass breakage No
Encapsulation: Loss of No
high-potential isolation
within CIGS solar cells and modules as well as individual layers, are discussed. Short
time effects, like buffer diffusion due to heat or illumination are not included, and
information about barriers, encapsulants, edge sealing and other ‘module constitu-
ents’ are omitted, unless an influence between the module constituents or the cell
materials has been observed.
30
Table 2.2: Summary of failure modes as observed for CIGS (modified but based on
reference [15]).
Failure modes CIGS Impacted Possible
specific physical parameters failure mechanisms
Cell degradation
Main junction: increase Yes Loss in fill factor, J sc Diffusion of dopant, impurities etc +
of recombination and V oc electromigration
Shunting Yes R shunt decreases Diffusion of metals, impurities etc.
Series resistance increase by Yes R s increases Corrosion, diffusion
TCO and Mo degradation
Delamination of back metal Yes J sc decrease Lamination stresses
contact
Module degradation
Interconnect resistance Yes R s increases Corrosion, electromigration
(ZnO:Al/Mo or Mo)
Interconnect degradation Yes R sh decreases Corrosion, electromigration
– shunting: across isolation
scribe
Busbar failure No R s increase or open Corrosion, electromigration
circuit
Solder joint No R s increase or open Fatigue, coarsening
circuit (alloy segregation)
Encapsulation delamination No Loss in fill factor, J sc Surface contamination, UV degrada -
and tion, hydrolysis of silane/glass bond,
possible open circuit warped glass, ‘dinged’ glass edges,
thermal expansion mismatch
Encapsulation: loss or hermet - No
ic seal
Encapsulation: glass breakage No
Encapsulation: Loss of No
high-potential isolation
within CIGS solar cells and modules as well as individual layers, are discussed. Short
time effects, like buffer diffusion due to heat or illumination are not included, and
information about barriers, encapsulants, edge sealing and other ‘module constitu-
ents’ are omitted, unless an influence between the module constituents or the cell
materials has been observed.
30